Why are native biodiversity and sustainability essential to biotrade in Peru?
Síguenos en:Google News
Biotrade is a business model that leverages native biodiversity as a driving force for sustainable economic development in the country.
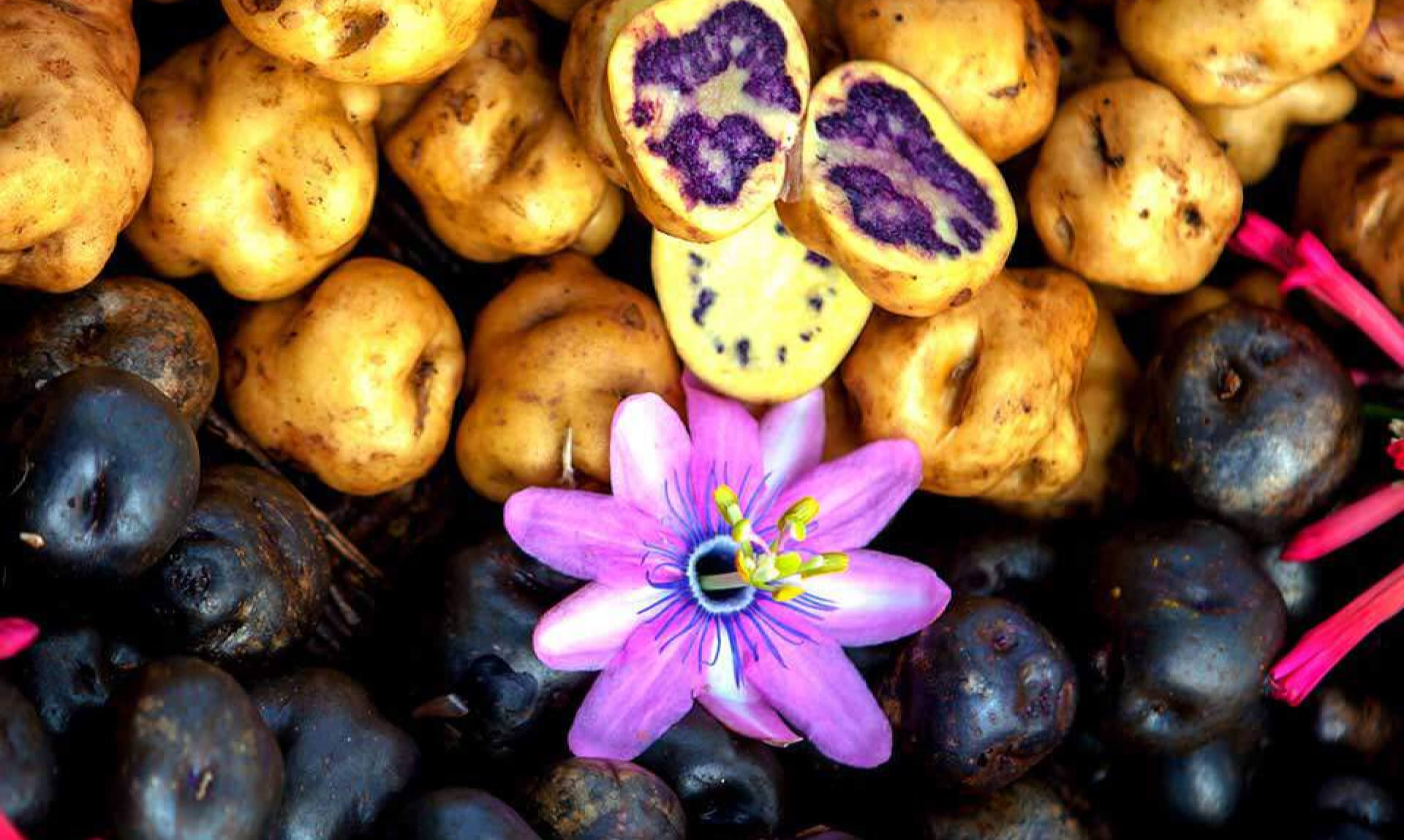
Peru is among the most megadiverse countries in the world. It boasts 84 of the 117 recognized life zones globally and 28 of the 32 existing climate types, making it a hotspot of extraordinary biodiversity. This abundance has earned Peru recognition from the United Nations as one of the 17 countries harboring over 70 % of the planet's biodiversity.
Biodiversity, which includes ecosystems, species, and genetic resources, is one of the planet's most precious assets. For Peru, as one of the world’s most biologically diverse countries, biotrade holds particular importance. This approach involves the production, transformation, and marketing of goods and services derived from native biodiversity, all guided by principles of environmental, social, and economic sustainability. The term "biotrade" was officially introduced in 1996 at the third Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity, establishing itself as a vital strategy for conserving natural resources while fostering sustainable development.
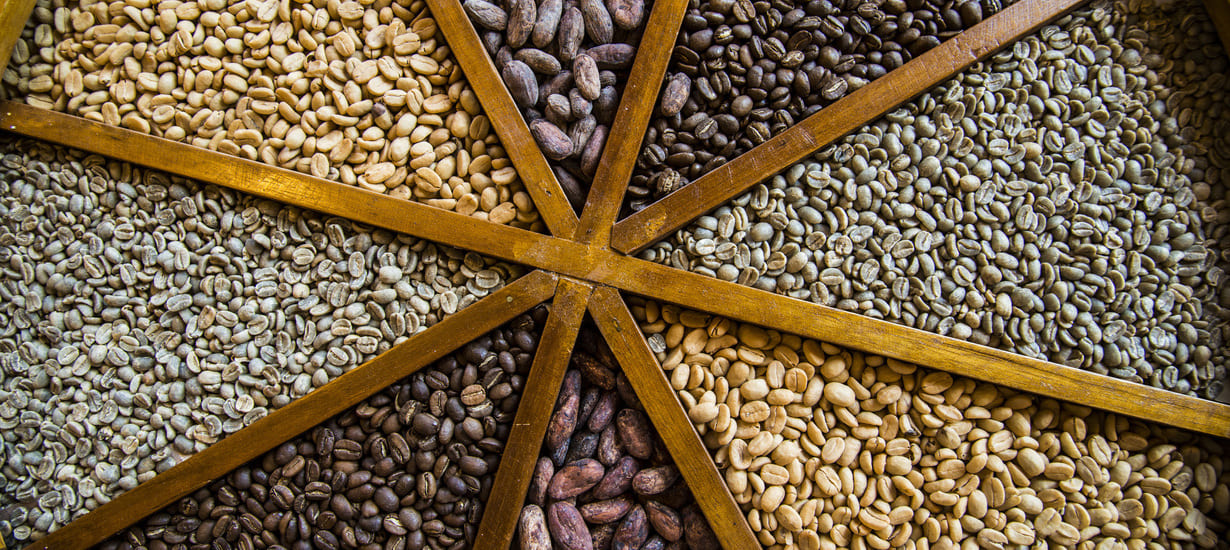
 Source: PROMPERÚ
Source: PROMPERÚ
Biodiversity: A cornerstone of biotrade
Biodiversity serves as the foundation of biotrade, offering not only an extensive range of raw materials for goods production but also essential ecosystem services like climate regulation and water purification. According to the Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean, Latin America harbors 40 % of the world's biodiversity, positioning the region as a global hub for biotrade. In Peru, products like quinoa are exported worldwide under rigorous sustainability standards, showcasing the potential of megadiverse nations to create competitive and responsible markets. In Peru alone, exports of such products have surpassed USD 500 million in FOB value, highlighting their significant economic impact.
The true value of biodiversity lies in the resources it offers, which drive national economic growth and support the most vulnerable communities. This unique advantage paves the way for emerging markets, fostering the sustainable trade of natural-origin products and unlocking new economic opportunities.
 Source: PROMPERÚ
Source: PROMPERÚ
Sustainability: The core of biotrade
In a world increasingly affected by climate change and biodiversity loss, sustainability stands as a cornerstone of biotrade. It entails the responsible management of natural resources, ensuring their renewal while safeguarding the habitats critical to maintaining ecological balance.
Sustainable practices in biotrade encompass the responsible use of resources, crop rotation, and the implementation of clean technologies. These approaches not only minimize environmental impact but also enhance the resilience of ecosystems to the effects of climate change.
Biotrade also addresses social and economic dimensions, ensuring that local communities receive fair benefits from the commercialization of products derived from biodiversity.
A clear example of this is the production of cocoa and chocolate in the Peruvian Amazon. Through biotrade projects, farming communities have adopted sustainable agricultural practices that not only enhance the quality of cocoa but also support the conservation of Amazonian forests, which are vital for global biodiversity. As a result, over 120,000 people involved in the cocoa value chain benefit from these initiatives, which have made Peruvian cocoa more competitive in international markets.